 |
| https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/cb/Planets2013.svg/2000px-Planets2013.svg.png |
Summary
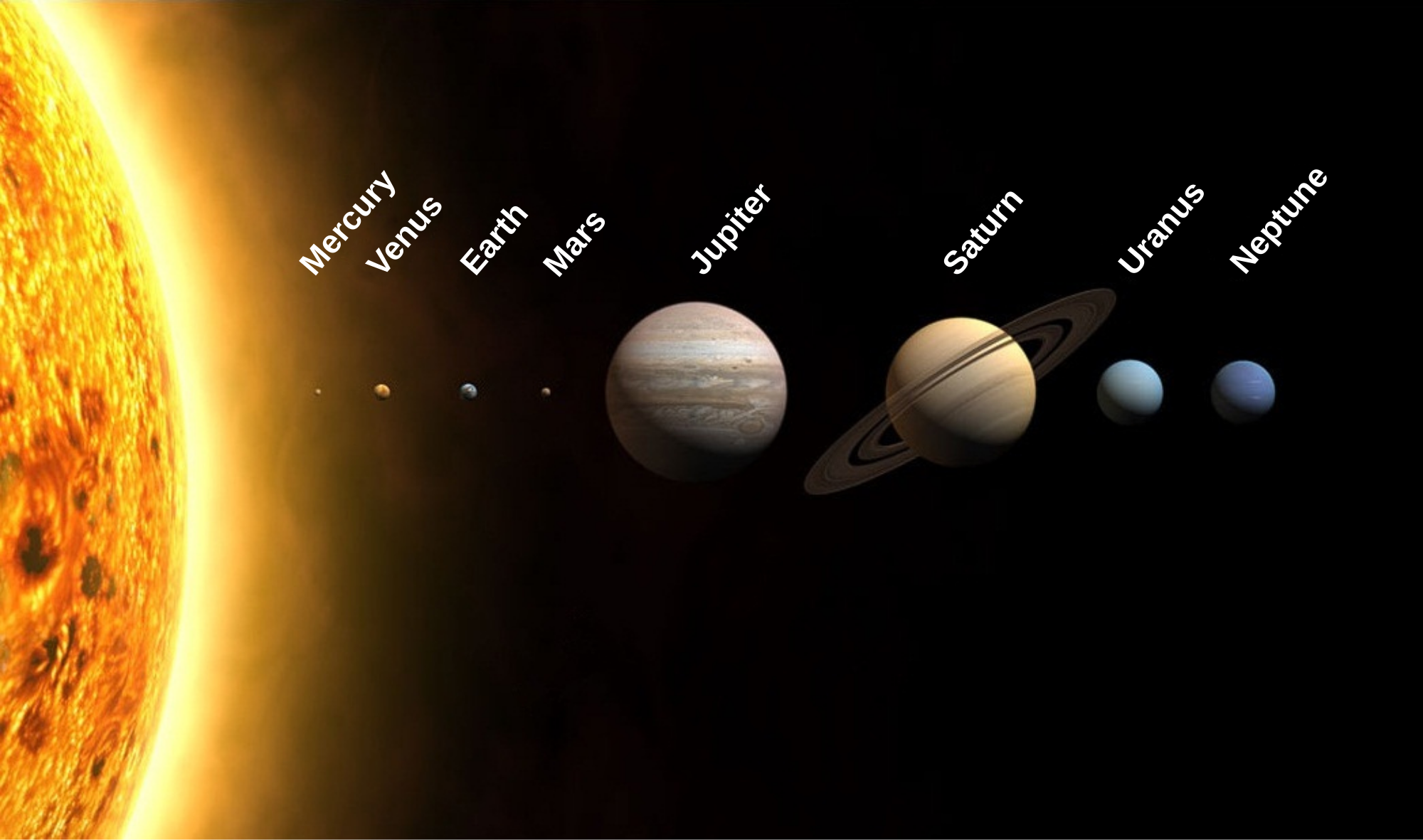
Our solar system lies within a galaxy called the Milky Way which contains billions of other stars. planets, and solar systems. In addition to that, our galaxy is only one out of hundreds of billions of other galaxies in the universe. There are three different kinds of galaxies. Spiral (like our Milky Way), Elliptical, and Irregular. The universe is an absurdly huge place. In order to measure things in space, we use a distance called light years. Light years are equal to how far light would travel in a year, roughly 6 trillion miles. Another unit of measurement astronomers use is AU or astronomical units. Astronomical units are used to measure distances within a solar system and are about the distance between the Earth and the Sun.
SP4: Analyzing and Interpreting Data
I analyzed and interpreted data when I read articles and watched videos to gather information on solar systems, galaxies, and more. By watching the videos, I gathered information which I then used to answer questions and fill out charts and tables on Formative. Finally, I completed a Mastery quest using all of the data and information I previously analyzed and gathered.
XCC: Cause and Effect
In space, there are many examples of cause and effect. One example is with our sun. When a solar flare occurs, particles from the sun are ejected into space. When conditions are right and the particles hit Earth and interact with the atmosphere and magnetic fields by being funneled near the poles, they can cause the air to glow creating the aurora. In addition to this, as the particles interact they can generate massive amounts of electricity in the Earth's crust which can cause overloads in the power grid and blackouts. Nuclear fusion and solar flares in the sun can have big effects on other planets like the Earth.
No comments:
Post a Comment